Solar Flares Today: A Comprehensive Analysis of Recent Solar Activity
Related Articles: Solar Flares Today: A Comprehensive Analysis of Recent Solar Activity
- 2025 BMW 1 Series: A Paradigm Shift In Compact Luxury
- Canada Summer Games 2025: A Comprehensive Schedule
- Printable 2025 Monthly Calendars: A Comprehensive Guide To Planning And Organization
- Lexus GX SUV 2025: The Pinnacle Of Rugged Refinement
- Jewish Holidays In 2025: A Comprehensive Guide
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Solar Flares Today: A Comprehensive Analysis of Recent Solar Activity. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Video about Solar Flares Today: A Comprehensive Analysis of Recent Solar Activity
Solar Flares Today: A Comprehensive Analysis of Recent Solar Activity
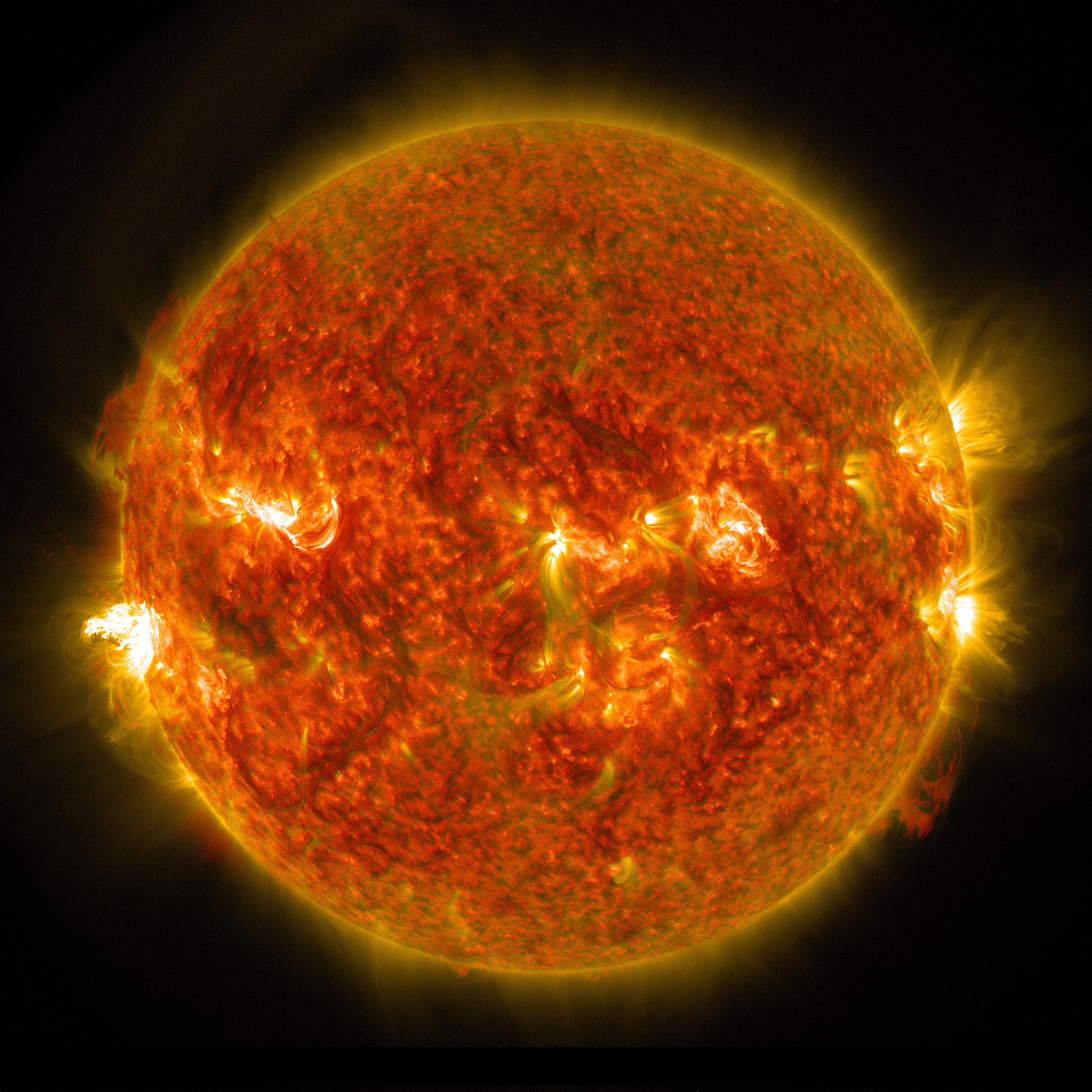

Introduction
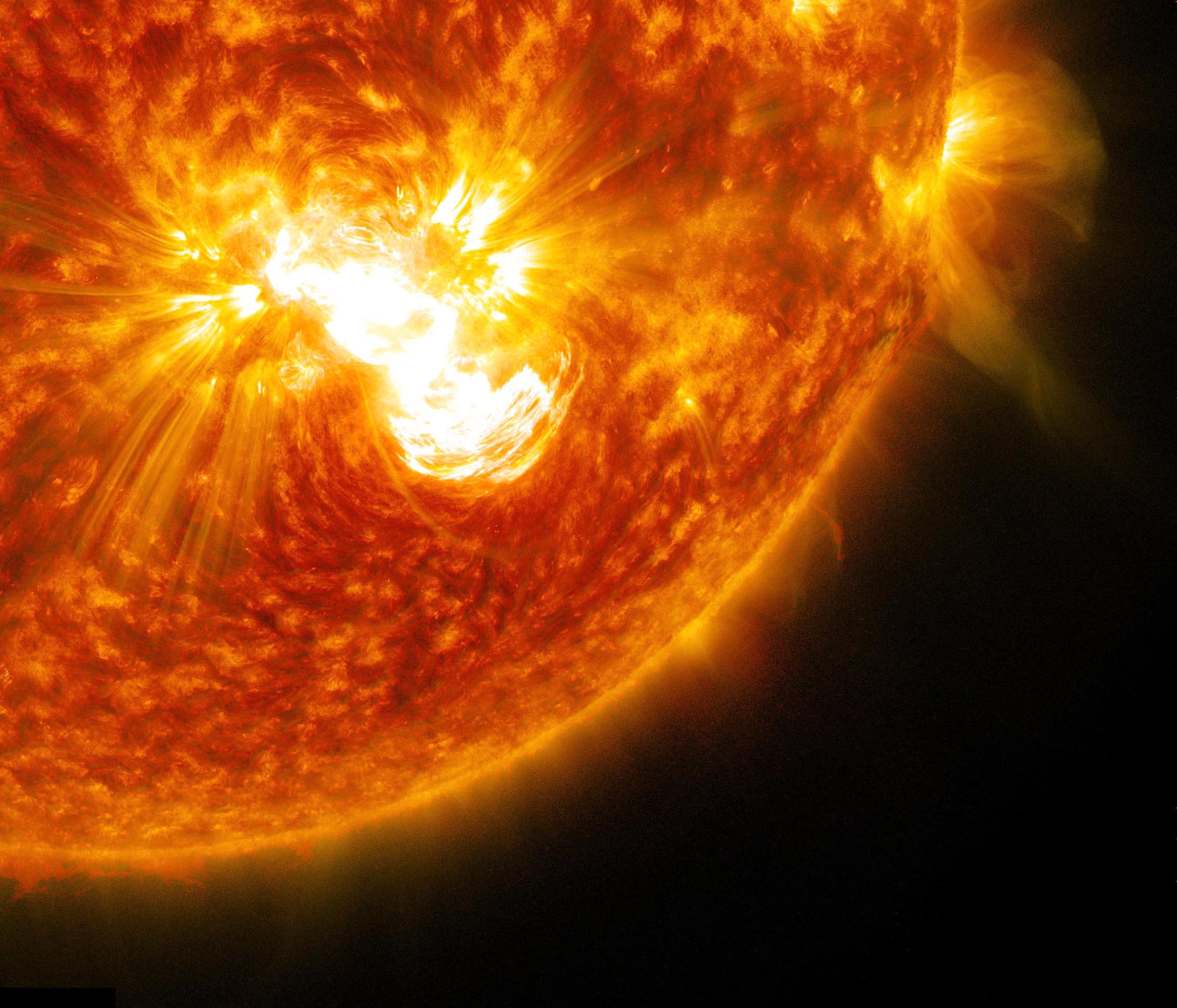
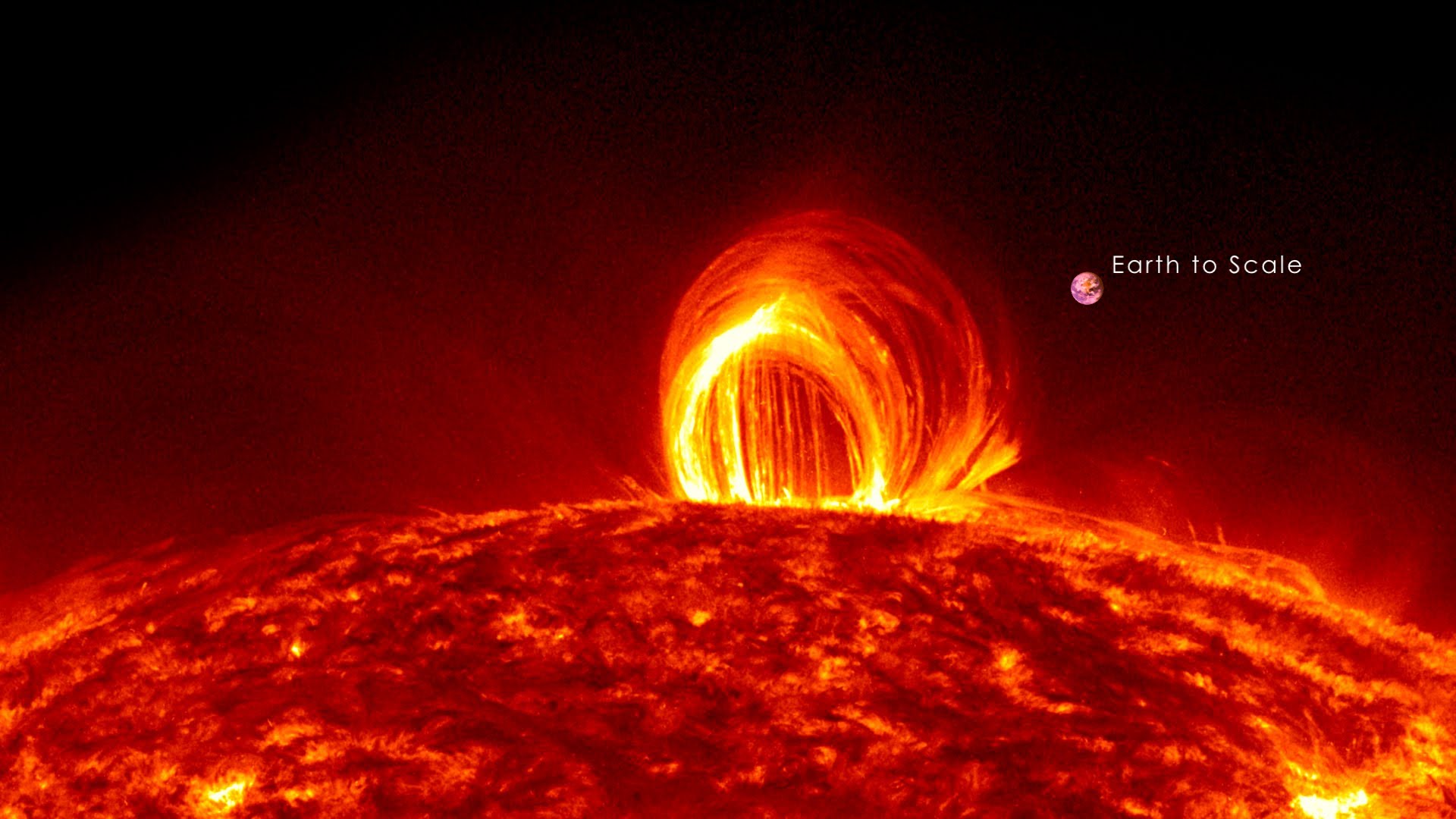
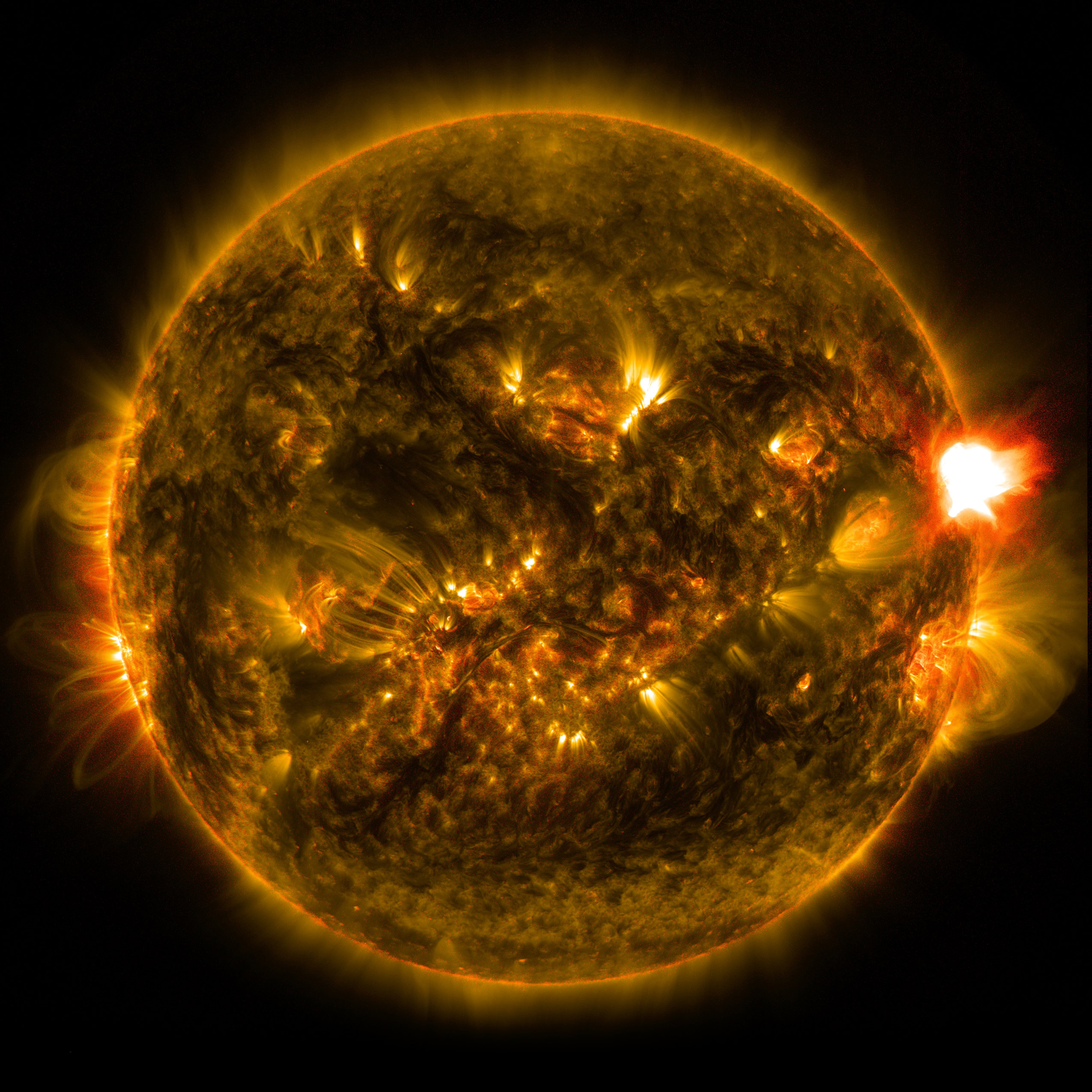
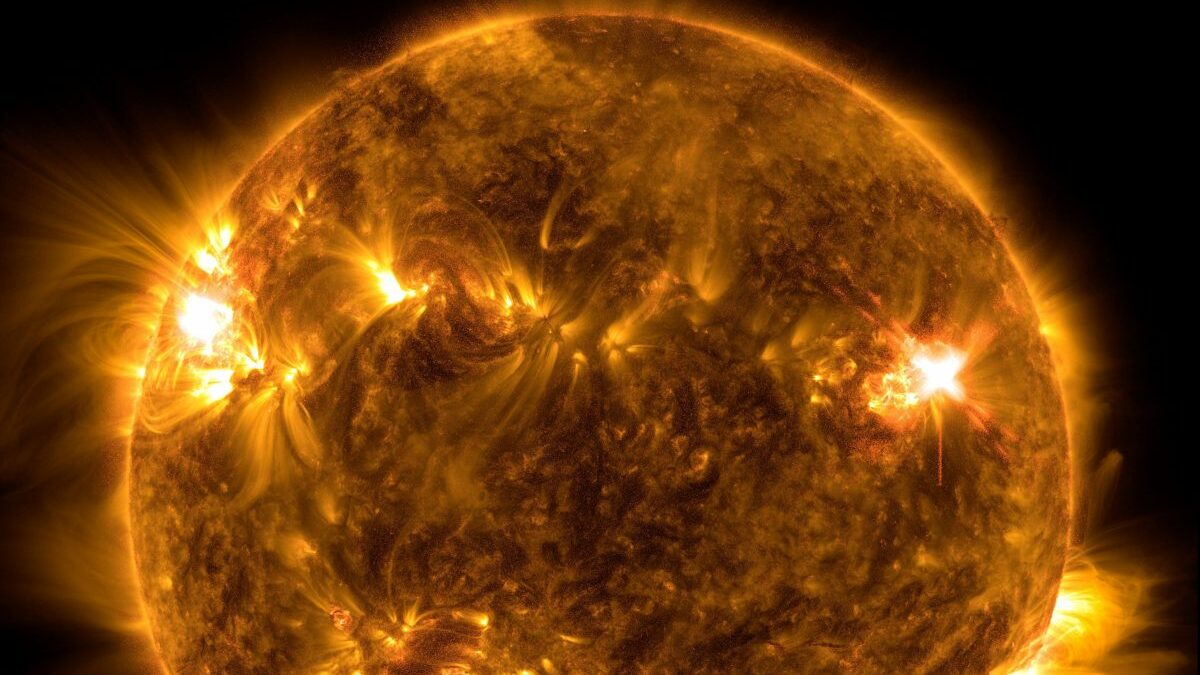
Solar flares are sudden and intense bursts of energy released by the Sun’s atmosphere. These eruptions can range in size and intensity, with the most powerful ones capable of disrupting Earth’s technology and infrastructure. Understanding solar flare activity is crucial for mitigating their potential impacts and ensuring the safety of our planet and its inhabitants. This article provides a comprehensive analysis of recent solar flare activity, including their characteristics, potential effects, and mitigation measures.
Characteristics of Solar Flares
Solar flares are classified into five categories based on their peak intensity, as measured in X-rays:
- A-Class Flares: The weakest type of flares, with peak intensities of 0.001-0.01 X-rays per square centimeter per second (X-rays/cm²/s).
- B-Class Flares: Moderate flares with peak intensities of 0.01-0.1 X-rays/cm²/s.
- C-Class Flares: Strong flares with peak intensities of 0.1-1 X-rays/cm²/s.
- M-Class Flares: Major flares with peak intensities of 1-10 X-rays/cm²/s.
- X-Class Flares: The most powerful flares, with peak intensities exceeding 10 X-rays/cm²/s.
Solar flares occur in active regions of the Sun, which are areas with strong magnetic fields. These regions are often associated with sunspots, which are dark areas on the Sun’s surface where the magnetic field is particularly intense. Flares erupt when the magnetic field lines in an active region become tangled and reconnect, releasing enormous amounts of energy in the form of X-rays, ultraviolet radiation, and charged particles.
Effects of Solar Flares
Solar flares can have a wide range of effects on Earth, both in space and on the ground.
- Space Weather Disturbances: Flares can disrupt the Earth’s magnetosphere, the magnetic field that protects the planet from charged particles. This can lead to geomagnetic storms, which can interfere with satellite communications, navigation systems, and power grids.
- Radio Blackouts: Flares can also cause radio blackouts, which can disrupt communications and navigation systems.
- Auroras: Charged particles from flares can interact with the Earth’s atmosphere, creating auroras, or Northern and Southern Lights.
- Radiation Hazards: Flares can emit harmful radiation, which can pose a health risk to astronauts and high-altitude aircraft passengers.
Recent Solar Flare Activity
In recent months, the Sun has been particularly active, with several major solar flares being observed. On September 6, 2023, an X1.2-class flare erupted from the Sun’s active region AR3182. This flare caused a geomagnetic storm that disrupted radio communications in some parts of the world.
On September 10, 2023, an even more powerful X2.2-class flare erupted from AR3182. This flare caused a widespread geomagnetic storm that affected satellite communications, navigation systems, and power grids.
Mitigation Measures
While solar flares are a natural phenomenon, there are steps that can be taken to mitigate their potential impacts. These measures include:
- Space Weather Monitoring: Scientists monitor solar activity to provide early warnings of potential flares.
- Satellite Hardening: Satellites can be equipped with shielding to protect them from radiation and charged particles.
- Power Grid Protection: Power grids can be upgraded with surge protectors and other measures to reduce the risk of disruptions.
- Public Education: Raising public awareness about solar flares and their potential effects can help people take precautions to protect themselves and their property.
Conclusion
Solar flares are a significant natural hazard that can have a wide range of effects on Earth. Understanding solar flare activity is essential for mitigating their potential impacts and ensuring the safety of our planet and its inhabitants. By monitoring solar activity, implementing mitigation measures, and raising public awareness, we can reduce the risks associated with solar flares and protect our critical infrastructure and technologies.







Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Solar Flares Today: A Comprehensive Analysis of Recent Solar Activity. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!