Schedule C (Form 1040) for 2025: A Comprehensive Guide for Sole Proprietors and Freelancers
Related Articles: Schedule C (Form 1040) for 2025: A Comprehensive Guide for Sole Proprietors and Freelancers
- Honda Civic 2025: A Glimpse Into The Future Of Compact Cars
- Disney World Marathon 2025: A Magical Race Experience Awaits
- Delhi Assembly Election 2025: A Battle For The Capital’s Soul
- PO Box 30100 Lansing MI: A Comprehensive Guide
- 2025 Subaru Forester: A Comprehensive Review
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Schedule C (Form 1040) for 2025: A Comprehensive Guide for Sole Proprietors and Freelancers. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Video about Schedule C (Form 1040) for 2025: A Comprehensive Guide for Sole Proprietors and Freelancers
Schedule C (Form 1040) for 2025: A Comprehensive Guide for Sole Proprietors and Freelancers
Introduction
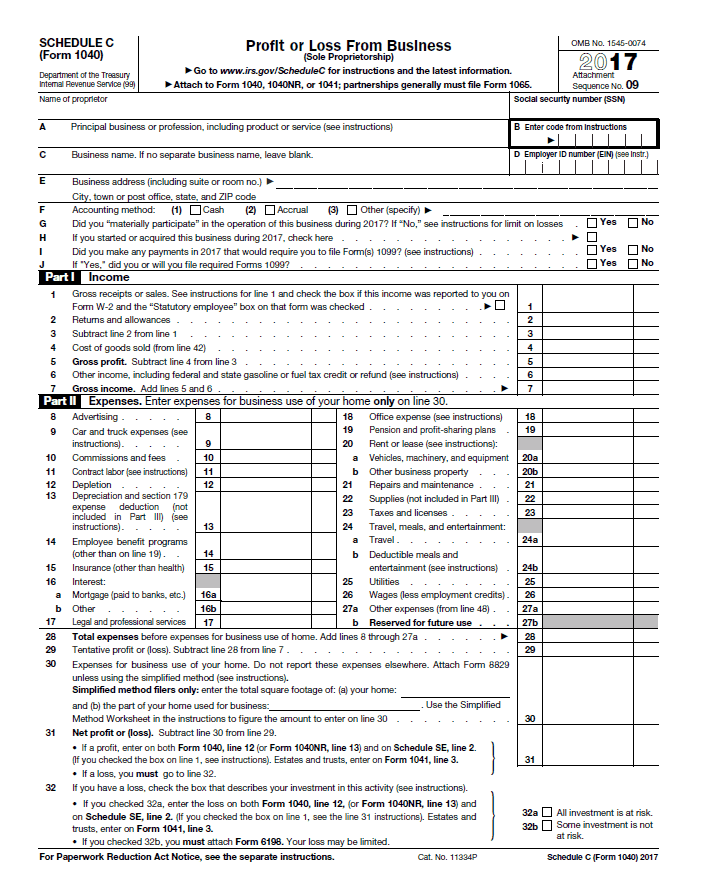
Schedule C (Form 1040) is an essential tax form for self-employed individuals, sole proprietors, and freelancers. It serves as a detailed record of business income and expenses, providing the Internal Revenue Service (IRS) with the necessary information to calculate the taxpayer’s taxable income and self-employment tax liability. Understanding and accurately completing Schedule C is crucial for ensuring compliance with tax laws and maximizing deductions. This comprehensive guide will provide a step-by-step breakdown of Schedule C, explaining each section and its purpose, and offering practical tips for accurate reporting.
Who Must File Schedule C?
Schedule C is required for any individual who operates a business as a sole proprietor or freelancer. This includes individuals who:
- Own and operate a business that is not incorporated or organized as a partnership or limited liability company (LLC).
- Provide services or sell products directly to customers.
- Receive income from activities that are not considered hobbies or personal use.
Step 1: Gather Your Information
Before you begin filling out Schedule C, it is essential to gather all the necessary information and documents, including:
- Business records, such as invoices, receipts, and bank statements.
- A list of all business expenses.
- A record of any income received from your business.
- Your Social Security number.
- Your business name and address.
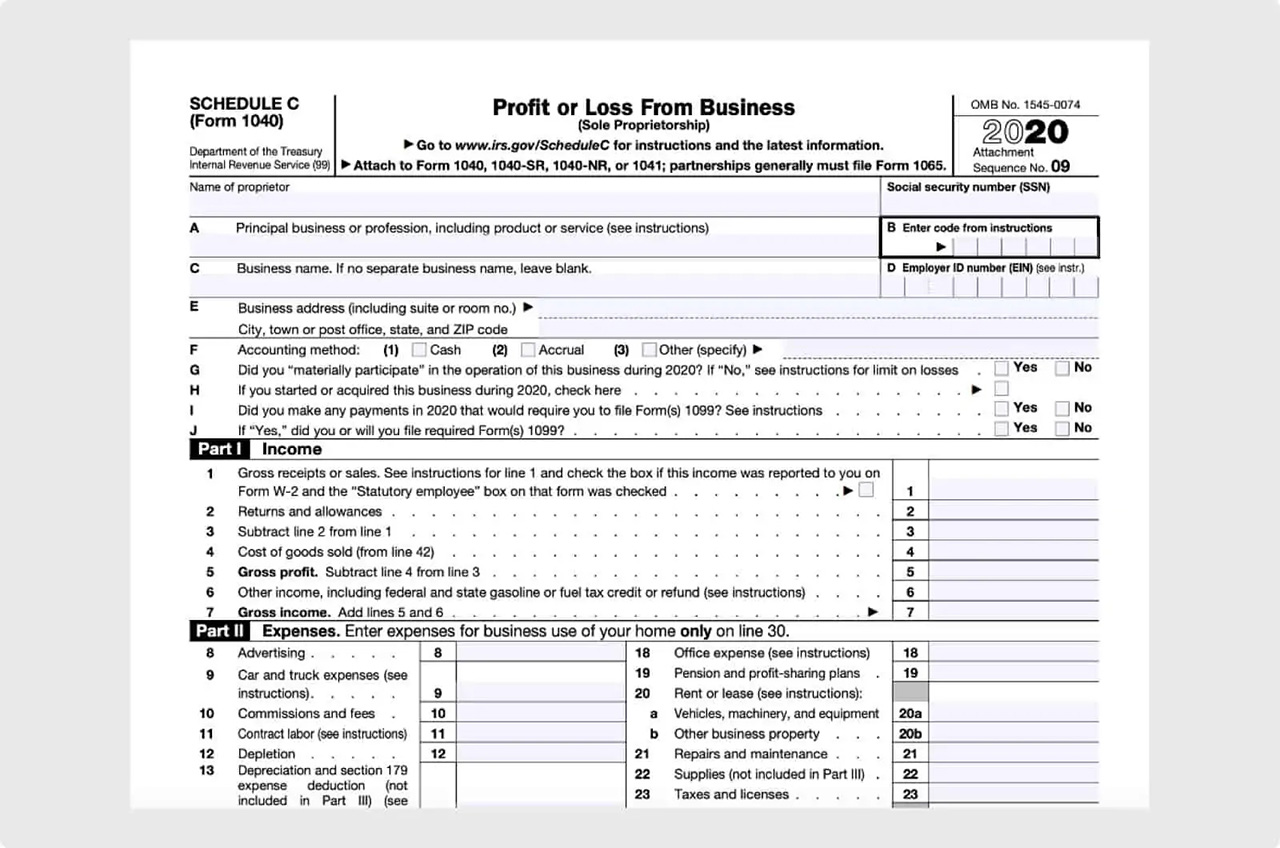
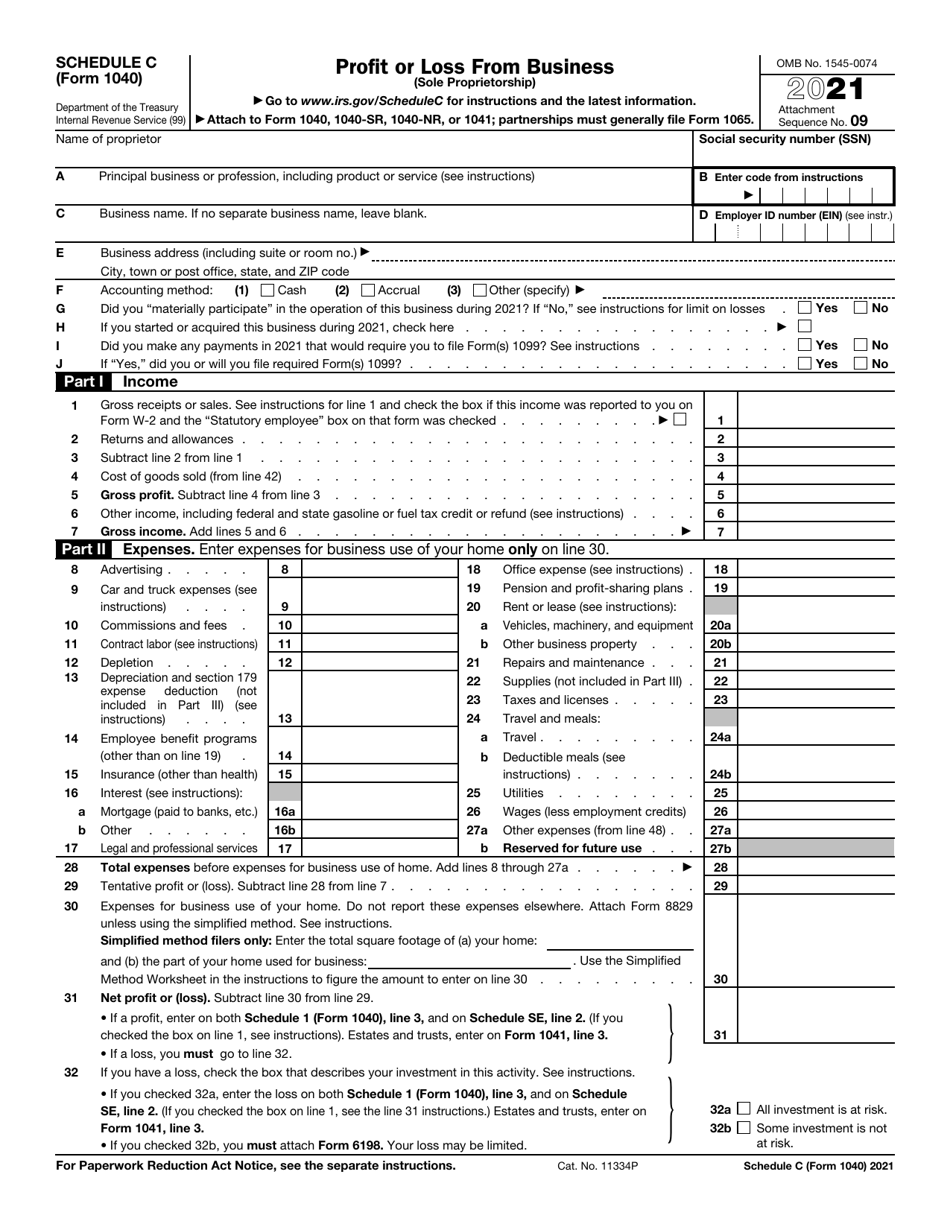
Step 2: Complete Part I: General Information
- Line 1: Name of Proprietor: Enter your full legal name as it appears on your Social Security card.
- Line 2: Principal Business or Professional Activity: Describe the primary activity of your business in a concise manner.
- Line 3: Business Name: Enter the official name of your business. If you operate under a different name, indicate it here.
- Line 4: Business Address: Provide the physical address of your business. If you operate from your home, enter your home address.
- Line 5: Accounting Method: Select the accounting method you use to track your business income and expenses. Most businesses use the cash method or the accrual method.
- Line 6: Method of Depreciation: Indicate the depreciation method you use for business assets.
- Line 7: Employer ID Number (EIN): Enter your EIN if you have one. An EIN is a unique nine-digit number assigned to businesses by the IRS.
Step 3: Complete Part II: Income
- Line 8: Gross Receipts or Sales: Enter the total amount of income you received from your business during the tax year.
- Line 9: Returns and Allowances: Subtract the amount of any returns or allowances you received from customers.
- Line 10: Cost of Goods Sold: If you sell products, enter the cost of goods sold (COGS). COGS includes the direct costs of producing the products, such as materials, labor, and overhead.
- Line 11: Gross Profit: Subtract COGS from gross receipts or sales to calculate your gross profit.
Step 4: Complete Part III: Expenses
- Line 12: Advertising: Enter the cost of advertising expenses incurred during the year.
- Line 13: Car and Truck Expenses: If you use a vehicle for business purposes, enter the deductible portion of car and truck expenses.
- Line 14: Commissions and Fees: Include the cost of commissions paid to sales representatives or fees paid to professionals.
- Line 15: Contract Labor: Enter the cost of labor paid to subcontractors or independent contractors.
- Line 16: Depreciation and Amortization: Include the depreciation and amortization expenses for business assets.
- Line 17: Employee Benefit Programs: Enter the cost of employee benefits, such as health insurance and retirement contributions.
- Line 18: Insurance: Include the cost of insurance premiums for business-related insurance policies.
- Line 19: Interest: Enter the amount of interest paid on business loans or other debt.
- Line 20: Legal and Professional Services: Include the cost of legal and professional services related to your business.
- Line 21: Office Expenses: Enter the cost of office supplies, equipment, and rent.
- Line 22: Pension and Profit-Sharing Plans: Include the cost of contributions to pension or profit-sharing plans.
- Line 23: Rent or Lease: Enter the cost of rent or lease payments for business premises.
- Line 24: Repairs and Maintenance: Include the cost of repairs and maintenance for business assets.
- Line 25: Supplies: Enter the cost of supplies used in the operation of your business.
- Line 26: Taxes and Licenses: Include the cost of business-related taxes and licenses.
- Line 27: Travel: Enter the cost of travel expenses incurred for business purposes.
- Line 28: Utilities: Include the cost of utilities, such as electricity, gas, and water.
- Line 29: Other Expenses: List any other deductible business expenses that do not fit into the categories above.
Step 5: Complete Part IV: Information on Your Vehicle
- Line 30: Vehicle Expenses: If you use a vehicle for business purposes, enter the percentage of business use.
- Line 31: Miles Driven for Business: Enter the total number of miles driven for business purposes.
Step 6: Complete Part V: Other Information
- Line 32: Principal Business Code: Enter the six-digit code that describes the primary activity of your business.
- Line 33: Did You Make Any Payments in 2025 That Related to a Business Activity Started or Acquired Before 2025? Answer "Yes" or "No."
- Line 34: If "Yes," Enter the Date You Started or Acquired the Business: Enter the date you started or acquired the business if you answered "Yes" to Line 33.
Step 7: Sign and Date Schedule C
- Line 35: Signature of Proprietor: Sign and date Schedule C.
- Line 36: Date: Enter the date you signed Schedule C.
Tips for Accurate Reporting
- Keep detailed records of all business transactions.
- Use a separate bank account for business purposes.
- Track expenses meticulously, even small ones.
- Use accounting software or consult with a tax professional to ensure accuracy.
- Keep receipts and invoices for all expenses and income.
- Be aware of the deductible expenses allowed by the IRS.
Conclusion
Schedule C (Form 1040) is a crucial tax form for sole proprietors and freelancers. By understanding and accurately completing Schedule C, you can ensure compliance with tax laws, maximize deductions, and avoid potential penalties. Remember to gather all necessary information, follow the step-by-step instructions carefully, and consult with a tax professional if needed. Accurate reporting on Schedule C is essential for maintaining good standing with the IRS and minimizing your tax liability.

:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/ScheduleC1-7818321402c0410ba4c212ca697c6227.jpg)
![]()

:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/ScreenShot2022-12-14at2.10.22PM-ed1958c9bbb642398aec3cacd721b244.png)
Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Schedule C (Form 1040) for 2025: A Comprehensive Guide for Sole Proprietors and Freelancers. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!