PEM Fuel Cell Technology: A Comprehensive Guide
Related Articles: PEM Fuel Cell Technology: A Comprehensive Guide
- Fast And Furious 11: The Epic Conclusion
- FIFA World Cup 2025: A Preview Of The Most Anticipated Soccer Event
- The 2025 Chevy Impala SS: A Legendary Muscle Car Returns
- When Is The Cannes Film Festival 2025?
- Ryder Cup Captains 2025: Zach Johnson And Luke Donald To Lead Respective Teams
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to PEM Fuel Cell Technology: A Comprehensive Guide. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Video about PEM Fuel Cell Technology: A Comprehensive Guide
PEM Fuel Cell Technology: A Comprehensive Guide

Introduction
Proton exchange membrane (PEM) fuel cells have emerged as a promising clean energy technology for various applications, including transportation, stationary power generation, and portable devices. This article provides a comprehensive overview of PEM fuel cell technology, including its principles of operation, components, advantages, challenges, and future prospects.
Principles of Operation
PEM fuel cells convert chemical energy from a fuel, typically hydrogen, into electrical energy through an electrochemical process. The basic components of a PEM fuel cell include:
- Anode: A porous electrode where hydrogen molecules are oxidized, releasing electrons and protons.
- Cathode: A porous electrode where oxygen molecules are reduced, consuming the electrons released from the anode.
- Proton exchange membrane (PEM): A thin, solid polymer electrolyte that allows protons to pass through but blocks electrons.
The hydrogen molecules at the anode are split into protons and electrons. The protons pass through the PEM to the cathode, while the electrons travel through an external circuit, generating an electrical current. At the cathode, the protons react with oxygen and electrons to form water.
Components of a PEM Fuel Cell
- Gas diffusion layer (GDL): A thin, porous layer that facilitates the transport of gases (hydrogen and oxygen) to and from the catalyst layer.
- Catalyst layer: A layer containing a catalyst, typically platinum or platinum alloys, which promotes the electrochemical reactions.
- Bipolar plate: A thin, conductive plate that separates individual fuel cells and collects the electrical current.
- End plates: Plates at the ends of the fuel cell stack that provide structural support and electrical connections.
Advantages of PEM Fuel Cells
- High efficiency: PEM fuel cells can achieve efficiencies of up to 60%, converting most of the fuel’s energy into electrical energy.
- Zero emissions: PEM fuel cells produce only water as a byproduct, making them environmentally friendly.
- Compact size: PEM fuel cells are relatively compact and lightweight, making them suitable for various applications.
- Quick startup: PEM fuel cells can start up and reach full power quickly, making them ideal for dynamic applications.
Challenges of PEM Fuel Cells
- Cost: PEM fuel cells are currently expensive to manufacture, particularly due to the use of platinum catalysts.
- Durability: PEM fuel cells can degrade over time, especially in harsh environments.
- Hydrogen storage: Hydrogen is a bulky and flammable gas, posing challenges for safe storage and transportation.
Future Prospects
Research and development efforts are focused on addressing the challenges and improving the performance of PEM fuel cells. Key areas of focus include:
- Cost reduction: Developing alternative catalyst materials and optimizing fuel cell design to reduce manufacturing costs.
- Durability improvement: Enhancing the stability of fuel cell components and developing mitigation strategies for degradation mechanisms.
- Hydrogen infrastructure: Establishing a reliable and cost-effective hydrogen supply chain to support widespread fuel cell adoption.
Applications of PEM Fuel Cells
- Transportation: PEM fuel cells are being used in fuel cell vehicles (FCVs), offering zero-emission, long-range transportation.
- Stationary power generation: PEM fuel cells can provide clean, efficient power for homes, businesses, and remote communities.
- Portable devices: PEM fuel cells are being integrated into portable power packs and other devices, providing extended battery life and eliminating the need for recharging.
Conclusion
PEM fuel cell technology offers significant potential for clean and efficient energy conversion. By addressing the current challenges and continuing to advance the technology, PEM fuel cells are poised to play a major role in the transition to a sustainable energy future. Their high efficiency, zero emissions, and compact size make them ideal for a wide range of applications, from transportation to portable devices. With ongoing research and development, PEM fuel cells are expected to become more affordable, durable, and widely adopted in the years to come.
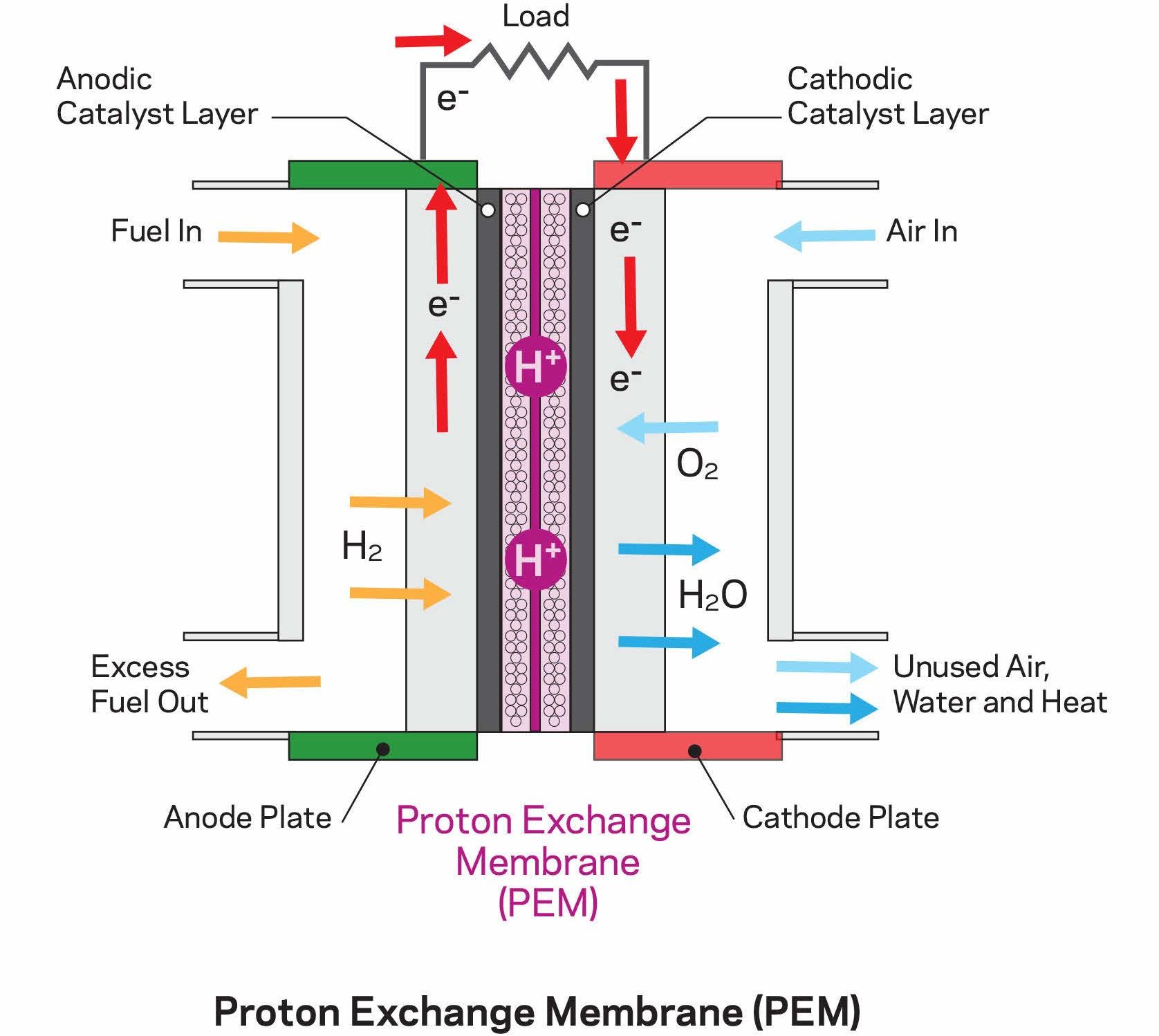

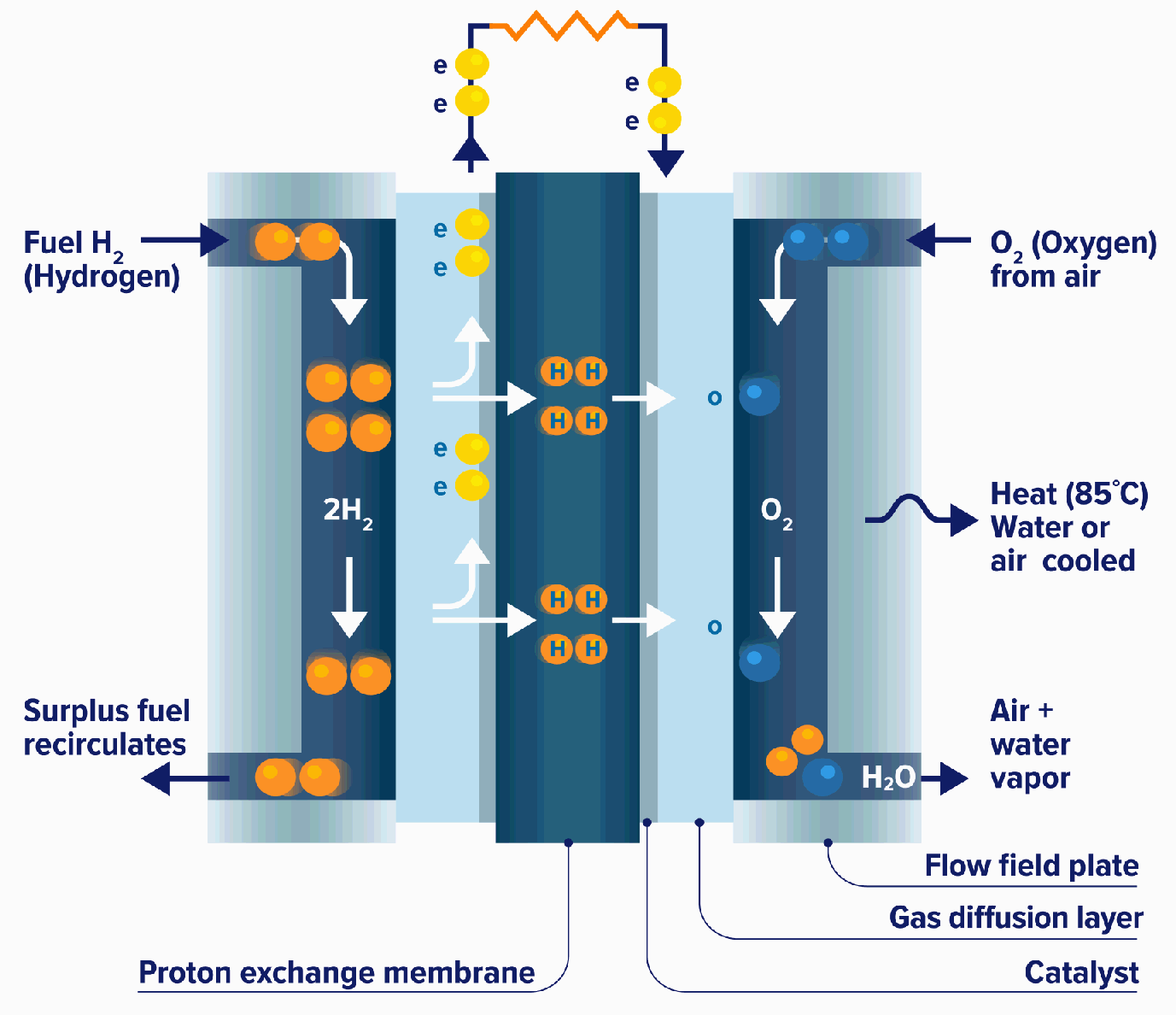
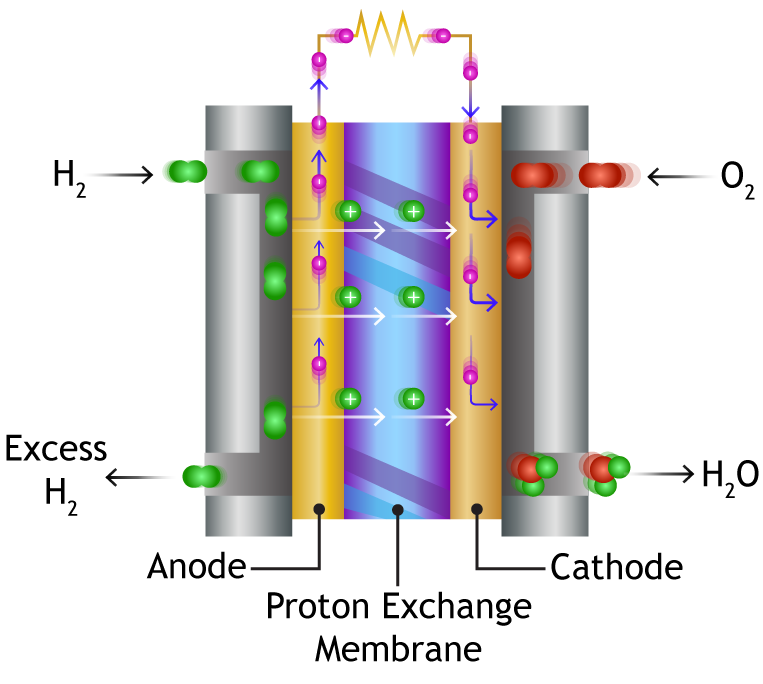
![Schematic of a PEM fuel cell [262]. Download Scientific Diagram](https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Yun_Wang25/publication/222679005/figure/fig1/AS:854934325055488@1580843635206/Schematic-of-a-PEM-fuel-cell-262.png)



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into PEM Fuel Cell Technology: A Comprehensive Guide. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!